Femto Photography – Catch Light Speed in Motion
Femtosecond (fs) is a measurement unit of time, equal to 10-15 second or 0. 000 000 000 000 001 second. Femto is the unit from the SI (International System of Unit) scale.
We may feel 1 second is a very short length of time in our daily life. But in science, there are even smaller measurement units out of our imagination:
1 second =1000 ms (milli second)
1 second = 1,000 000 μs (micro second)
1 second = 1 000 000 000 ns (nano second)
1 second = 1 000 000 000 000 ps (piko second)
1 second = 1 000 000 000 000 000 fs (femto second)
We know light travels about 300 000 metre per second, or 300 km per second. By using smaller measurement like femtosecond, we can work out that light travels about 300 nano metre ( or 0.000 000 3 metre) in 1 femtosecond (300 000 /1 000 000 000).
In 1964 Dr Harold Eugene ”Doc” Edgerton from MIT used a high-speed camera filmed a bullet hitting through an apple. At a million frames per second, the camera was able to slow down the bullet, revealing its mechanics and processes that occur when it hits the apple.
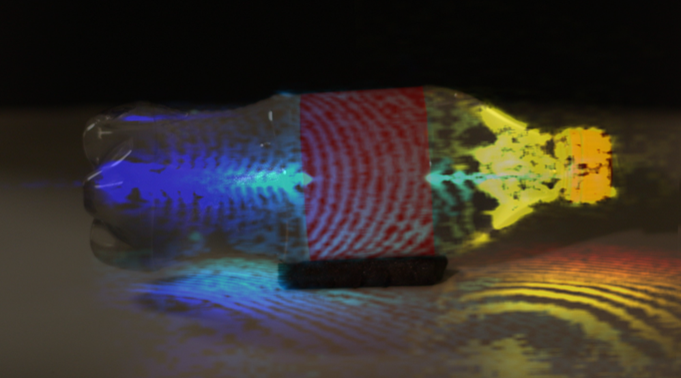
In this video, a laser beam travels like a bullet, at the speed of light go through a coke bottle. It is 1 million times faster than ordinary bullets, lasts only several femtoseconds (10^15fs).
What we see is that the time has been 10 billion time lapsed. If we use ordinary bullets to repeat this experiment, then it will take us more than a year to see the bullets move from one end of the coke bottle to the other end of the bottle.
We can watch how photons interact with matter; the way photons are absorbed, the way they are reflected, even their physical effect on water as these phontons cause little ripples to scatter about.
It takes light to travel:
- 18 milliseconds to travel between New York to London
- 0.13 seconds to circumnavigate the equator of the Earth
- 1.4 seconds to travel to the moon from Earth
- 8.4 minutes to travel from the Sun to the Earth
- 4.15 hours to travel from the Sun to Neptune, the most distant planet in our solar system
- 17 hours to travel to the current location of the Voyager 1 probe, which is the farthest man-made object in space
- 0.8 years to travel from the Earth to the Oort Cloud, which marks the boundary of our solar system
- 4.2 years to travel to Earth from Proxima Centauri, the nearest star from our Sun.
- 100 000 years to travel across the entire span of the Milky Way galaxy
- 2.5 million years to travel to us from our closest galaxy Andromeda galaxy
- 11 billion years to travel to the new found blob, one of the most distant structrues in the universe.
Point being, light (photons) is super freaking fast - the fastest traveling particle we know of, which makes Femto-Photography all the most impressive.
Watch the TED talk by Ramesh Raskar: Imaging at a trillion frames per second


Comments
Post a Comment